Study of antibiotic resistance and genetic Identification of clinical isolate of Escherichia coli and Evaluation of frequency of metalobetalactamas antibiotic resistance Gene by PCR method
کد: G-1024
نویسندگان: Maryam Adabi © ℗
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
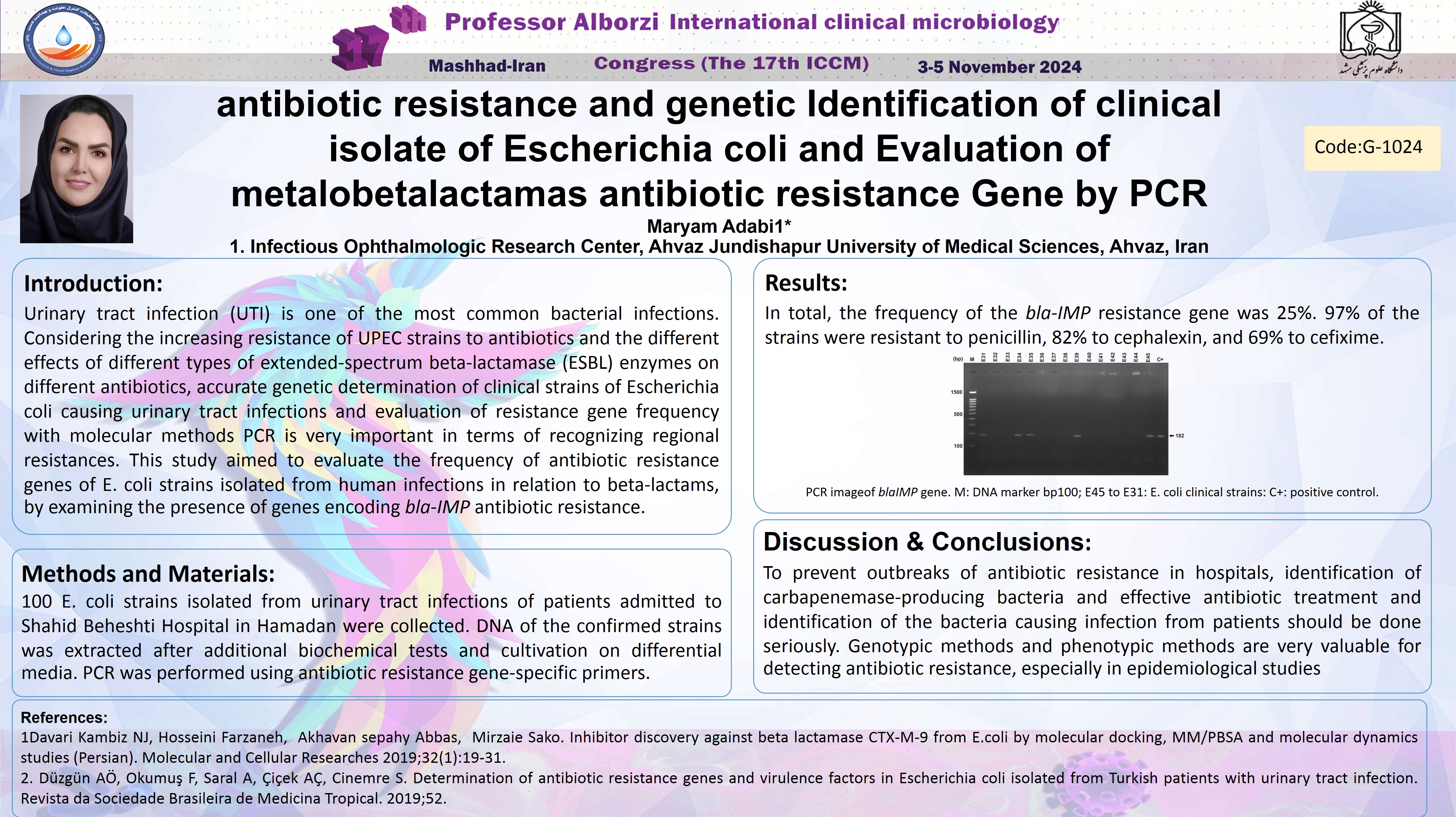
Study of antibiotic resistance and genetic Identification of clinical isolate of Escherichia coli and Evaluation of frequency of metalobetalactamas antibiotic resistance Gene by PCR method Maryam Adabi 1* 1 Infectious Ophthalmologic Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran Objective: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common bacterial infections. Among the types of hospital infections, urinary tract infection caused by Escherichia coli is the most important and prevalent and constitutes about 75-90% of the isolated cases. E. coli is responsible for 80-90% of community-acquired urinary tract infections and 40-50% of hospital-acquired infections and is called uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Considering the increasing resistance of UPEC strains to antibiotics and the different effects of different types of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) enzymes on different antibiotics, accurate genetic determination of clinical strains of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections and evaluation of resistance gene frequency with molecular methods PCR is very important in terms of recognizing regional resistances. This study aimed to evaluate the frequency of antibiotic resistance genes of E. coli strains isolated from human infections in relation to beta-lactams, by examining the presence of genes encoding bla-IMP antibiotic resistance. Material and Methods: 100 E. coli strains isolated from urinary tract infections of patients admitted to Shahid Beheshti Hospital in Hamedan were collected. DNA of the confirmed strains was extracted after additional biochemical tests and cultivation on differential media. PCR was performed using antibiotic resistance gene-specific primers. Results: In total, the frequency of the bla-IMP resistance gene was 25%. 97% of the strains were resistant to penicillin, 82% to cephalexin, and 69% to cefixime. Conclusion: To prevent outbreaks of antibiotic resistance in hospitals, identification of carbapenemase-producing bacteria and effective antibiotic treatment and identification of the bacteria causing infection from patients should be done seriously. Genotypic methods and phenotypic methods are very valuable for detecting antibiotic resistance, especially in epidemiological studies.
کلمات کلیدی
Keywords: Urinary tract infection, E. coli, antibiotic resistance, beta-lactam, cephalexin