بررسی بیان ژن¬های افلاکس MexCD-OprJ و MexEF-OprN در جدایه¬های بیمارستانی P. aeruginosa
کد: G-1029
نویسندگان: Mehdi Pourjafar © ℗, Leila Shokrzadeh
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
خلاصه مقاله
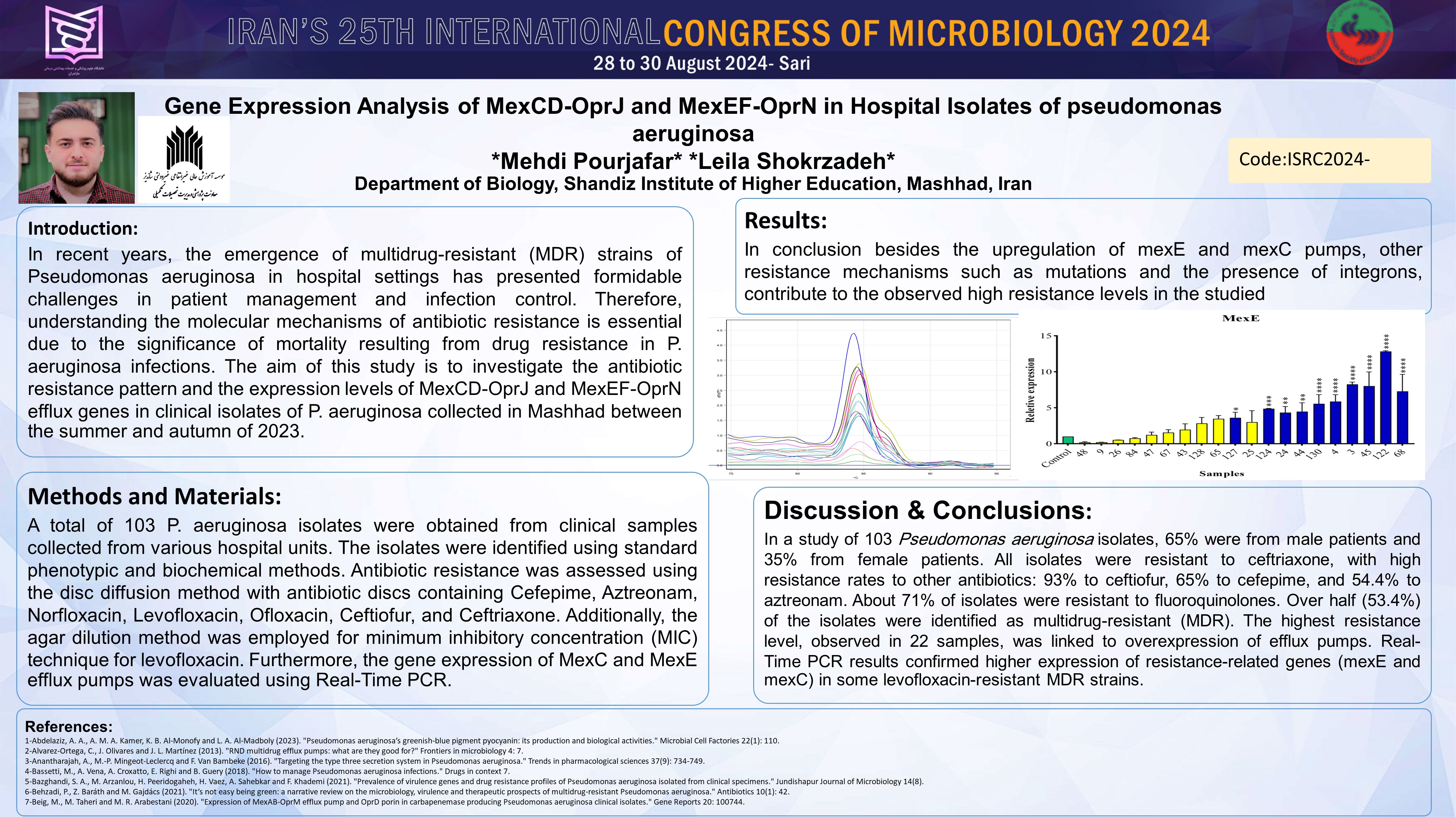
In recent years, the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital settings has presented formidable challenges in patient management and infection control. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance is essential due to the significance of mortality resulting from drug resistance in P. aeruginosa infections. The aim of this study is to investigate the antibiotic resistance pattern and the expression levels of MexCD-OprJ and MexEF-OprN efflux genes in clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa collected in Mashhad between the summer and autumn of 2023. A total of 103 P. aeruginosa isolates were obtained from clinical samples collected from various hospital units. The isolates were identified using standard phenotypic and biochemical methods. Antibiotic resistance was assessed using the disc diffusion method with antibiotic discs containing Cefepime, Aztreonam, Norfloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Ceftiofur, and Ceftriaxone. Additionally, the agar dilution method was employed for minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) technique for levofloxacin. Furthermore, the gene expression of MexC and MexE efflux pumps was evaluated using Real-Time PCR. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: In a study of 103 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates, 65% were from male patients and 35% from female patients. All isolates were resistant to ceftriaxone, with high resistance rates to other antibiotics: 93% to ceftiofur, 65% to cefepime, and 54.4% to aztreonam. About 71% of isolates were resistant to fluoroquinolones. Over half (53.4%) of the isolates were identified as multidrug-resistant (MDR). The highest resistance level, observed in 22 samples, was linked to overexpression of efflux pumps. Real-Time PCR results confirmed higher expression of resistance-related genes (mexE and mexC) in some levofloxacin-resistant MDR strains. In conclusion besides the upregulation of mexE and mexC pumps, other resistance mechanisms such as mutations and the presence of integrons, contribute to the observed high resistance levels in the studied strains.
کلمات کلیدی
Hospital infections, MexCD-OprJ and MexEF-OprN, P. aeruginosa, Multidrug-resistant